Abstract
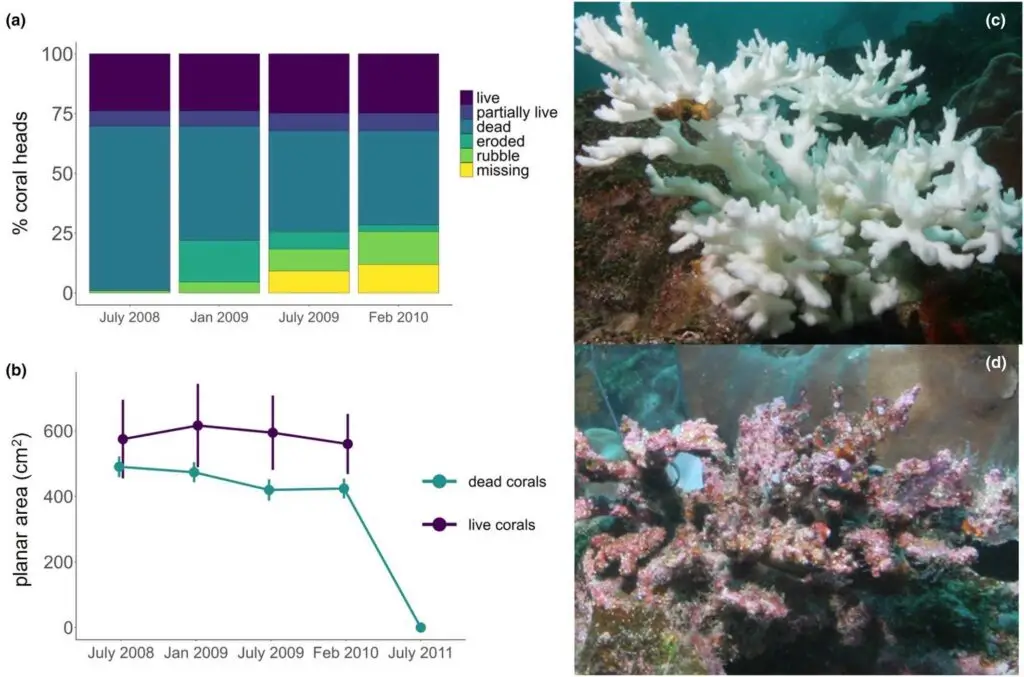
During a cold La Niña period (August 2007–January 2008) in the central Galápagos archipelago, 70% of Pocillopora branching corals were severely bleached across three long-term monitoring sites, affording an opportunity to examine its impact on the persistence of these corals and their associated community of fish and mobile macroinvertebrates. Using a time series empirical approach, we tagged and tracked the fate of 96 coral heads and their associates. When surveyed in July 2008, recovered live and dead corals that were previously severely bleached supported similar levels of species richness (randomized observed and estimated Chao 1). By contrast, richness on the surviving live corals remained fairly stable, while Chao 1 estimated richness on dead corals underwent a nearly 50% increase between July and January 2009, thereafter declining to 50% of originally surveyed richness by February 2010. This nonlinear change in species richness was largely due to an influx and decline in opportunistic generalists including pencil urchin bioeroders, gastropod snails, and hermit crabs that colonized dead corals and fed on sessile invertebrates and algae that had initially recruited to dead and undefended coral substrate. Thus, dead corals retained high overall species richness until live corals had recovered, after which richness declined as dead corals eroded and disintegrated (July 2011). Live corals attracted a less speciose but stable assemblage of mutualistic xanthid crabs and fishes that increased in abundance over time with the recovery and growth of live coral tissue. Overall, coral status (live/dead), planar area and maximum branch length predicted the number of species associated with each colony. The delayed diversity loss of associated species following La Niña disturbance to a foundation species represents a local extinction debt of 32–49-month duration. A better understanding of the scale of extinction debt in foundational marine ecosystems is needed to quantify the breadth of impacts of climate oscillations on biodiversity and ecosystem functioning.
Read the article in the link: https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1111/maec.12767