Marine iguanas have lower metabolic rates during El Niño
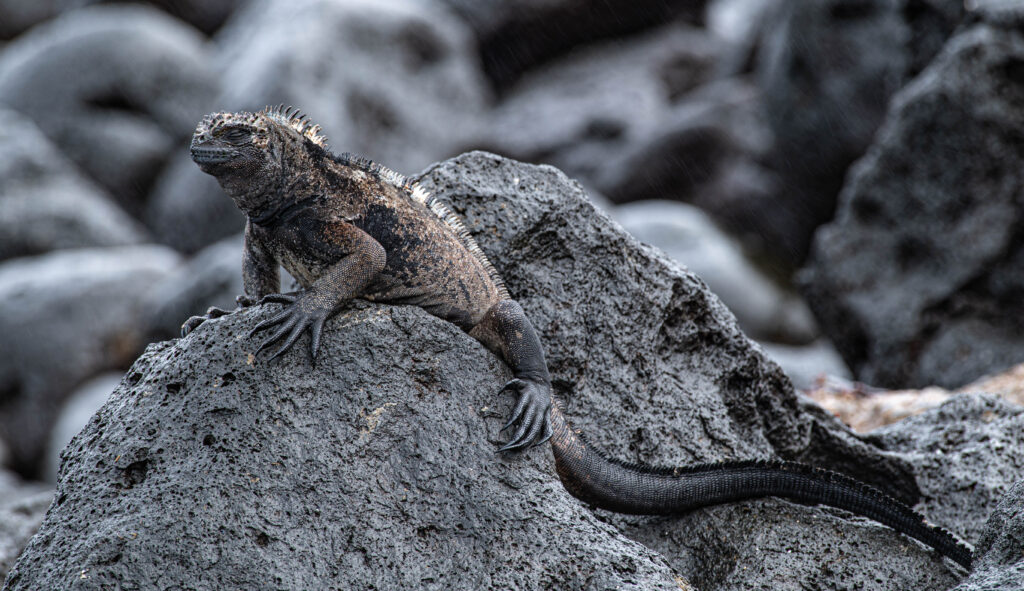

Marine iguanas of the Galápagos (Amblyrhynchus cristatus) are the only lizard species in the world that feeds in the ocean, relying almost exclusively on algae. During the El Niño climate event, rising ocean temperatures reduce the availability of this food source, leading to periods of scarcity. This research examines how these climatic changes affect their physiology and body condition.
High-Quality De Novo Genome Assembly for the Galápagos Endemic Lava Gull Using Oxford Nanopore Technologies
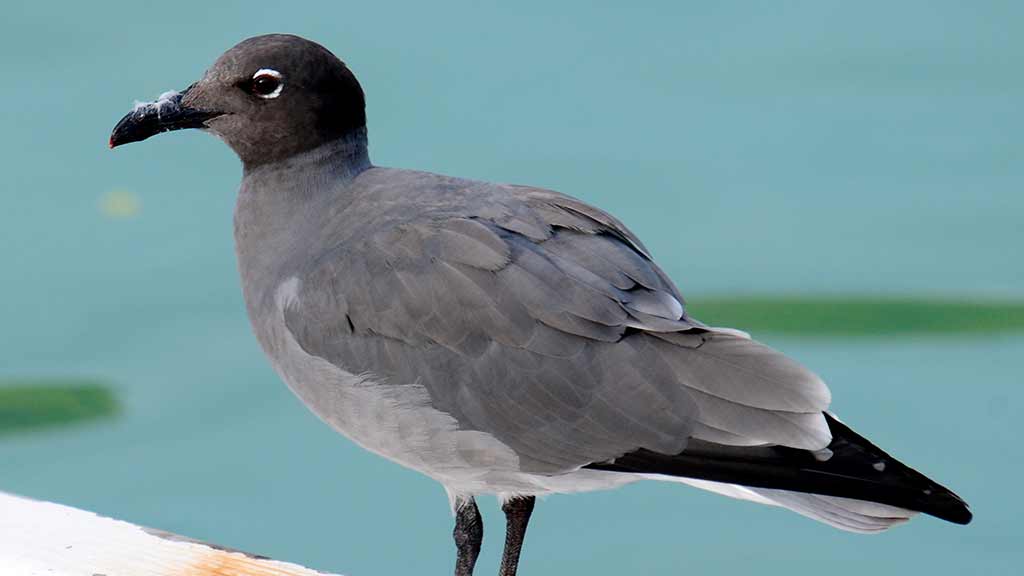

The lava gull (Leucophaeus fuliginosus), an endemic species of the Galápagos Islands, is the rarest gull in the world, with an estimated population of 300 to 600 individuals, making it a conservation priority.
Balancing post-pandemic recovery and resilience in the Galápagos: how beliefs in ecosystem fragility impact residents’ attitudes toward tourism and conservation knowledge and compliance

This research examines the challenges faced by the Galápagos Archipelago in the context of post–COVID-19 tourism recovery, as well as the need to balance economic development with the conservation of a highly fragile ecosystem.
Genomic and biogeographic patterns of endemic geckos in the Galapagos Islands reveal population structure and species delimitation on inhabited islands
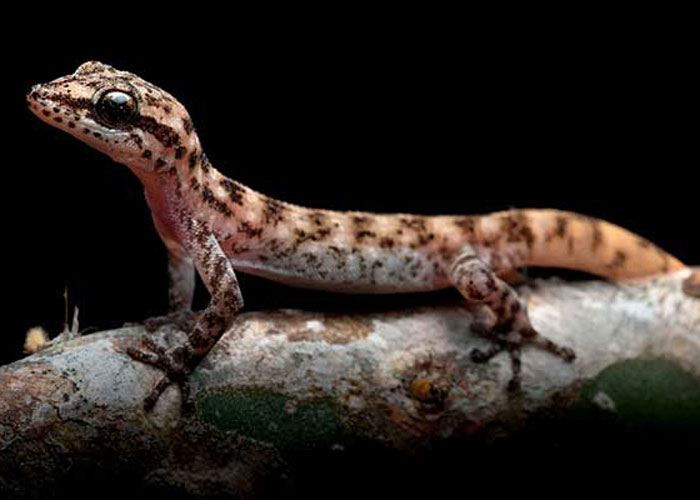

Oceanic islands such as Galápagos are privileged settings for studying how species originate and diverge. In this context, the endemic geckos of the genus Phyllodactylus play an important ecological role and, at the same time, remain poorly known from a genetic perspective.
Animals and Land Cover/Land Use Change: A Remote Sensing – Galápagos Islands Assessment
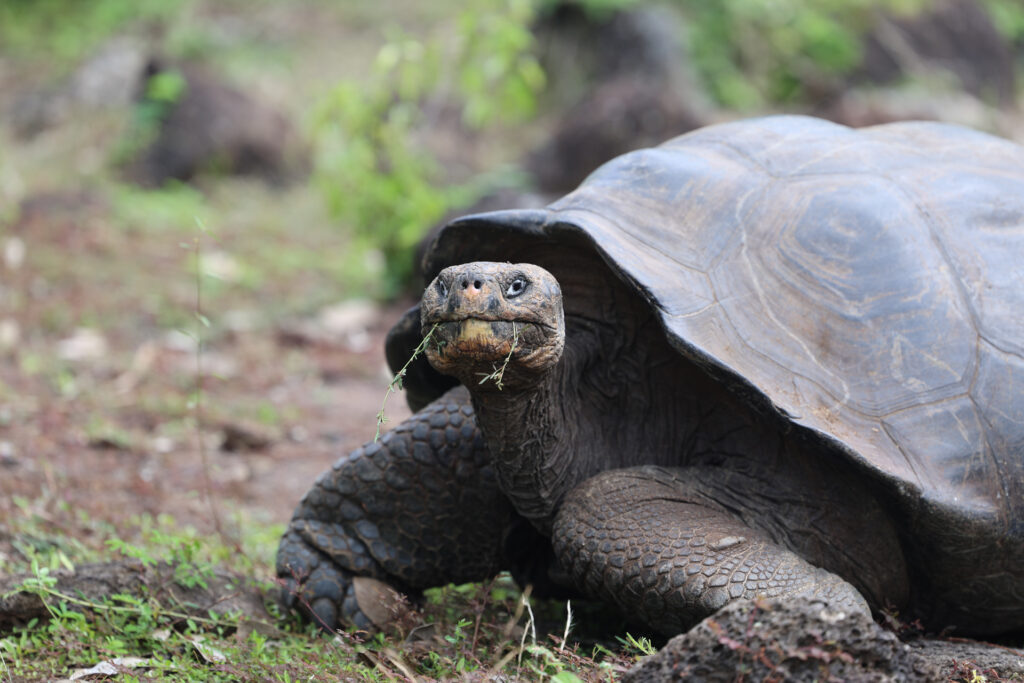

The ecosystems of Galápagos are in constant transformation due to the interaction between natural processes, animals, and human activities. This research analyzes how different species, both native and introduced, influence the islands’ landscape through their movements, feeding habits, and behavior, and how these changes can be observed using digital environmental monitoring tools.
Reproductive timing and intensity in a Galápagos intertidal mollusc are modulated by thermal phases

This study analyzes how variations in sea temperature influence the reproduction of the canchalagua (Radsia goodallii), an endemic mollusk of the Galápagos Islands with ecological and socio-economic importance for local artisanal fisheries. Understanding its reproductive patterns is essential for developing management and conservation strategies that ensure the sustainability of the species.
Exploring pathogenic fungi to control the invasive plant Rubus niveus on San Cristóbal Island, Galápagos
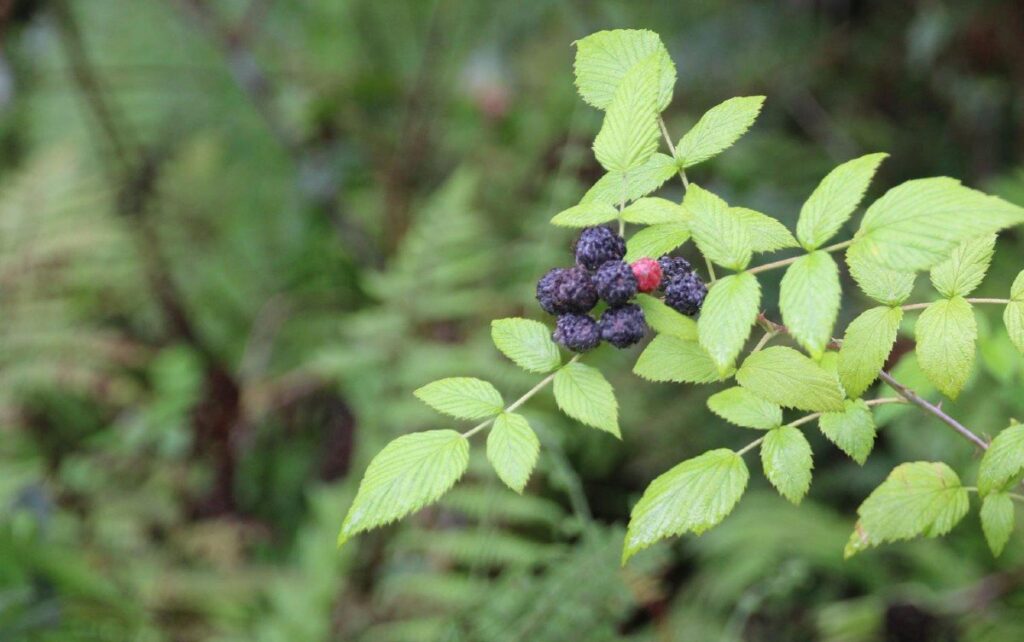

The invasive bramble (Rubus niveus) is one of the main threats to the native flora of the Galápagos Islands. It currently occupies around 30,000 hectares in the highlands, where it displaces native vegetation and affects biodiversity.
First Report of Anaplasma phagocytophilum in Galapagos: High Prevalence in Dogs and Circumstantial Evidence for the Role of Rhipicephalus linnaei as Vector
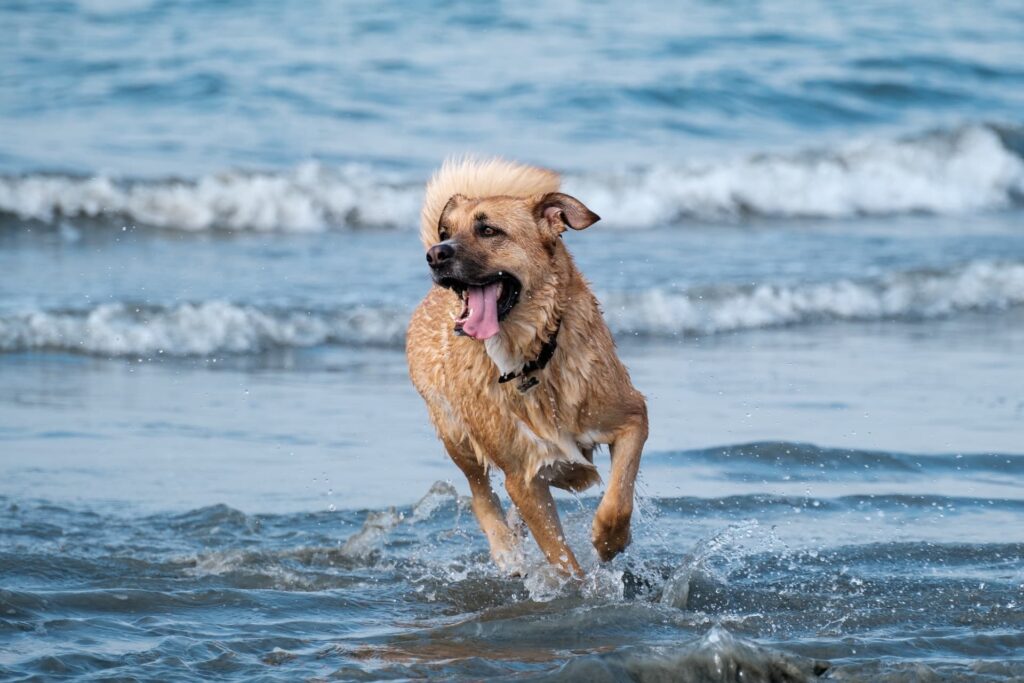

The Galápagos Islands host a unique biodiversity but face increasing threats from emerging diseases. Among them, tick-borne pathogens such as Anaplasma spp. are of concern due to their potential impact on both domestic animals and wildlife. Understanding their presence and transmission dynamics is essential for conservation and public health.
Drivers of Marine Phytoplankton Diversity and Connectivity in the Galápagos Archipelago Spanning an ENSO Cycle
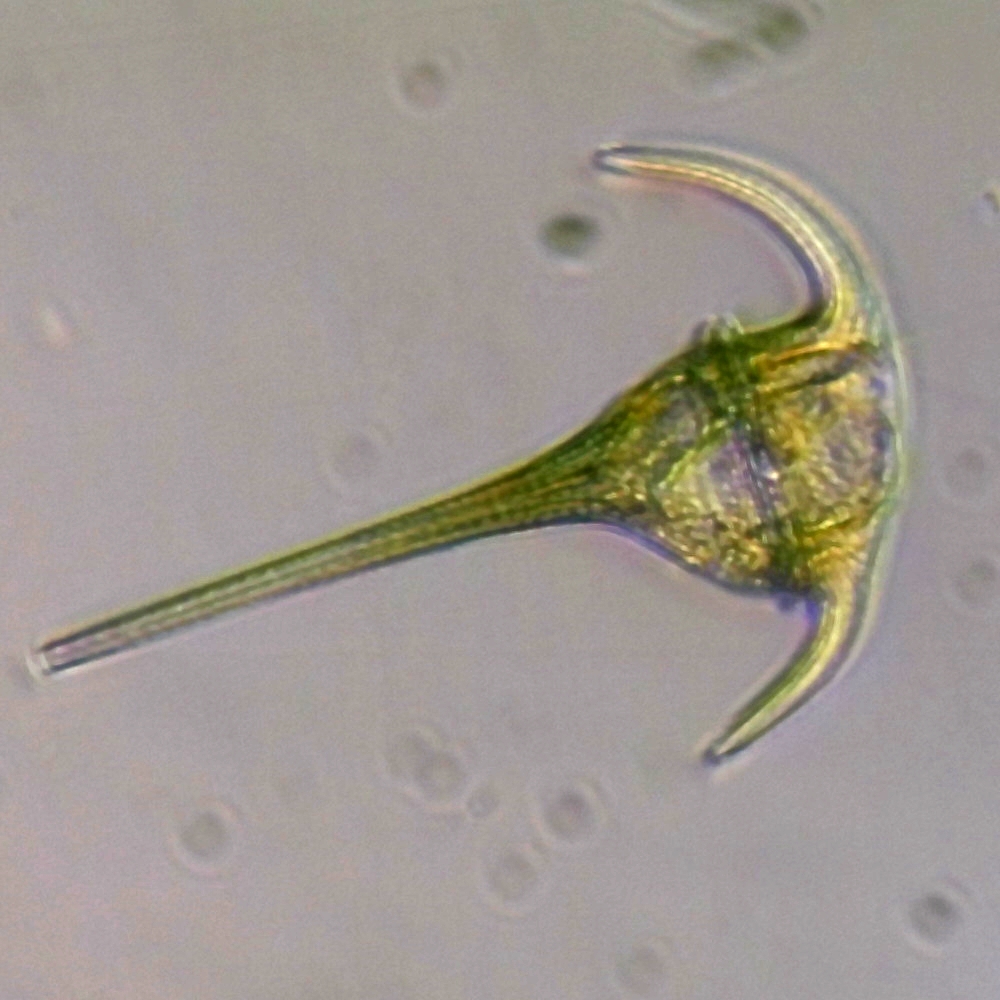
Phytoplankton form the foundation of marine food webs, and their diversity strongly influences ocean ecosystem health. In the Galápagos Islands, ocean currents and climate variability linked to the El Niño-Southern Oscillation (ENSO) shape these communities, driving changes in productivity and connectivity.
Heterogeneous preferences for cleaner maritime transportation in the tourism sector: A choice experiment from the Galápagos Islands

Maritime transport is essential for tourism in the Galápagos Islands, but it also represents a significant source of pollution.This study explores tourists’ willingness to pay for cleaner propulsion technologies, electric and hybrid, as alternatives to internal combustion engines, aiming to promote more sustainable tourism in this fragile ecosystem.


