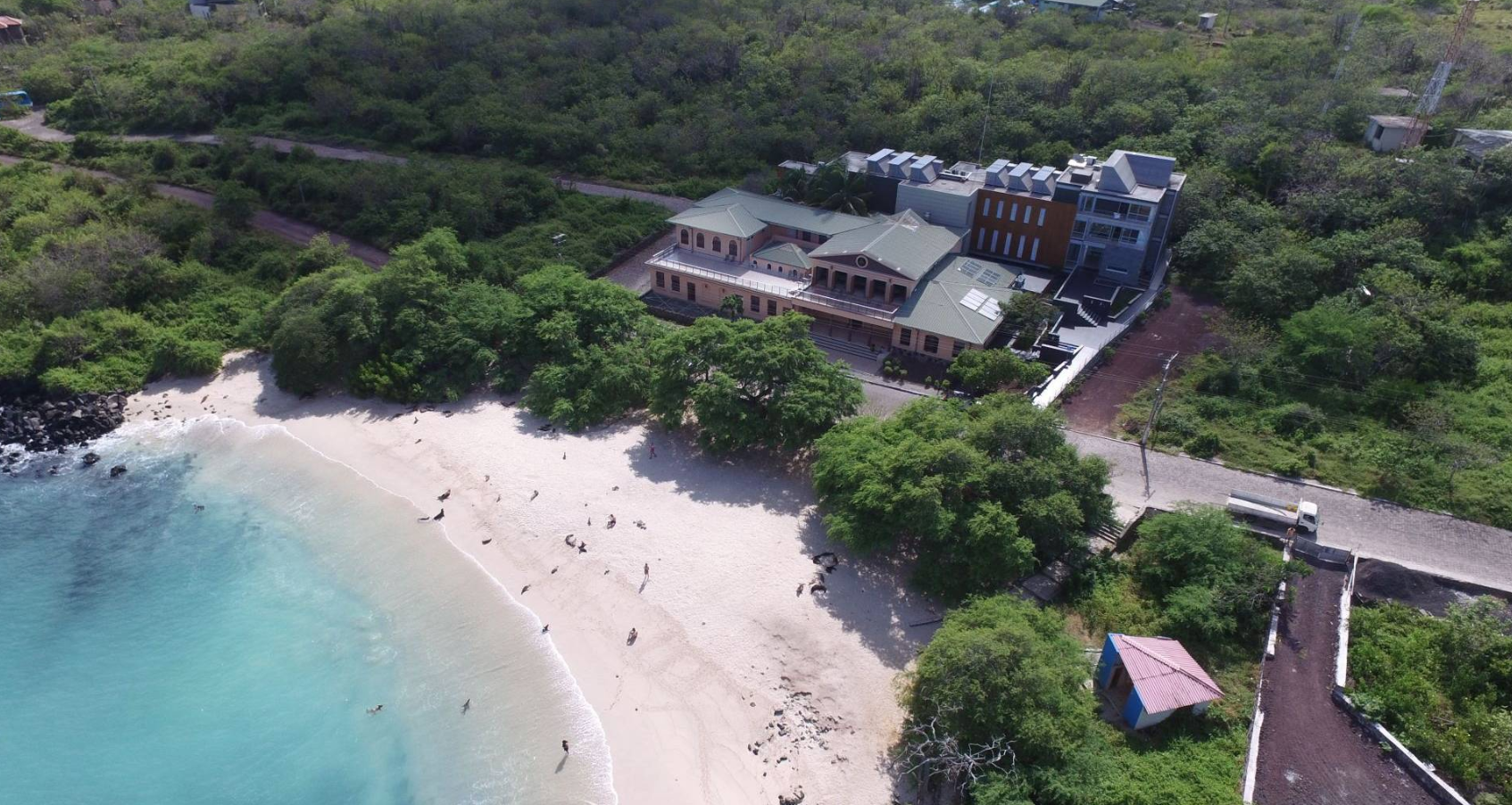
Universidad San Francisco de Quito and the Oceanogràfic Foundation launched a program to monitor the health of marine species in the Galápagos Islands

A team of veterinarians from the Oceanografic Foundation traveled to Puerto Baquerizo Moreno to establish a veterinary health surveillance.
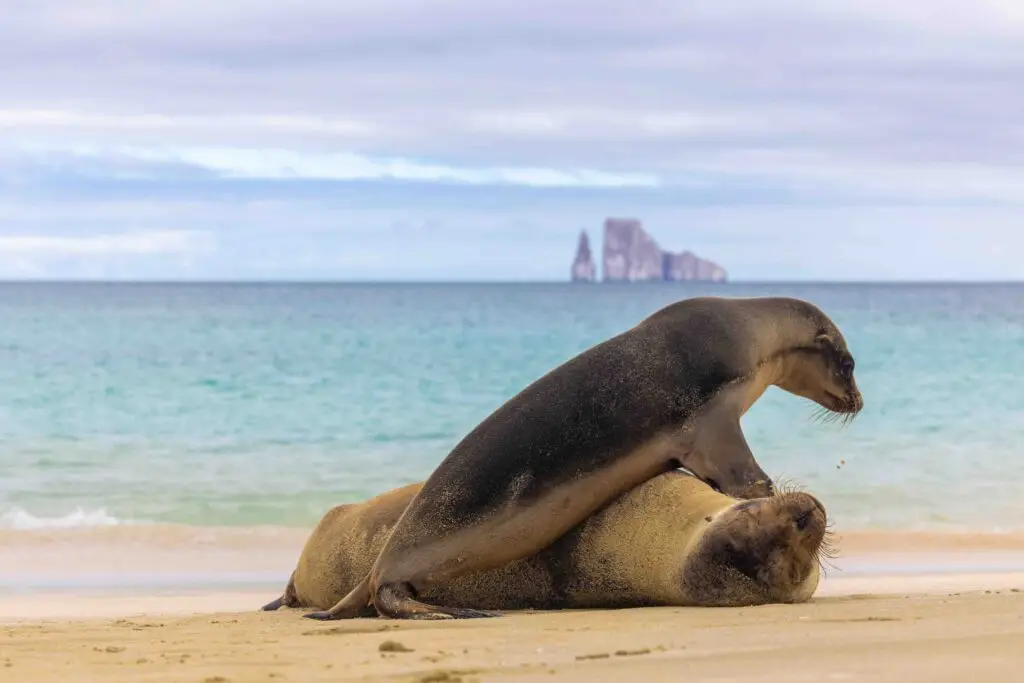
Time-calibrated phylogeny and full mitogenome sequence of the Galapagos sea lion (Zalophus wollebaeki) from scat DNA

The Galapagos sea lion, Zalophus wollebaeki, is an endemic and endangered otariid, which is considered as a sentinel species of ecosystem dynamics in the Galapagos archipelago.
La Niña-related coral death triggers biodiversity loss of associated communities in the Galápagos
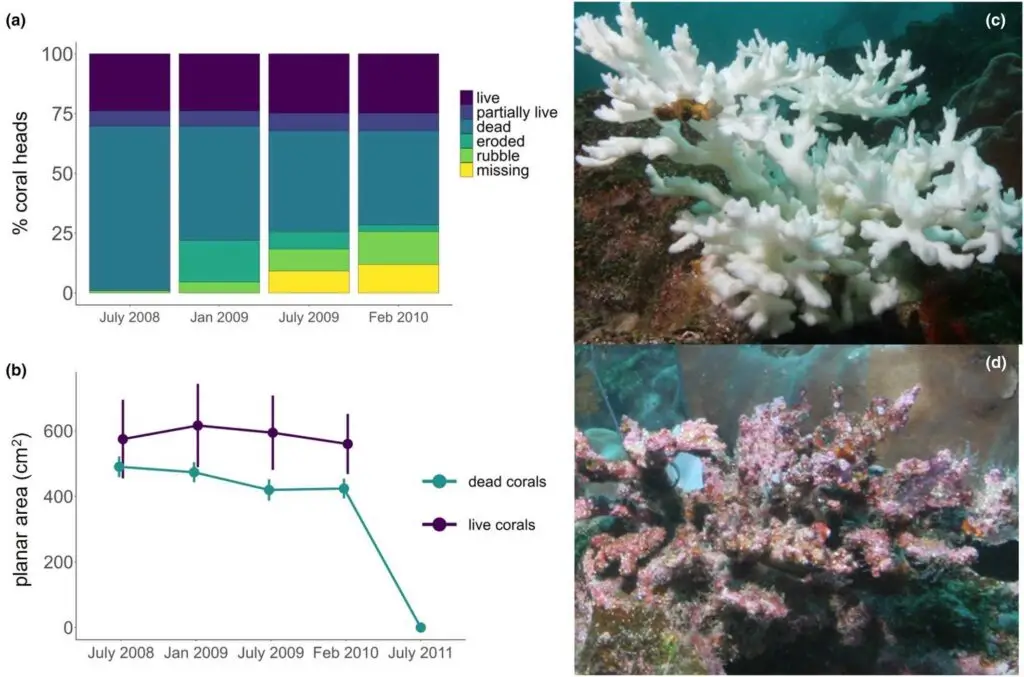
During a cold La Niña period (August 2007–January 2008) in the central Galápagos archipelago, 70% of Pocillopora branching corals were severely bleached across three long-term monitoring sites.
Hematology and Biochemistry of the Española Lava Lizard (Microlophus delanonis)
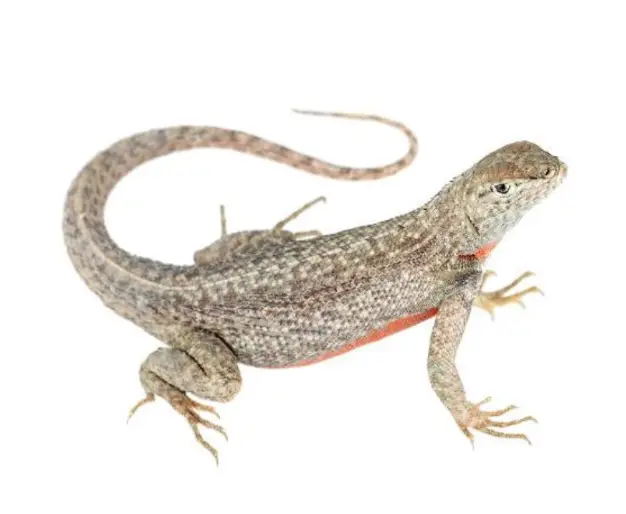

This paper presents novel baseline health parameters on the Española lava lizard (Microlophus delanonis). Morphologic parameters measured included body weight, snout-vent length, and temperature.
Detection and quantification of microplastic pollution in the endangered Galapagos sea lion
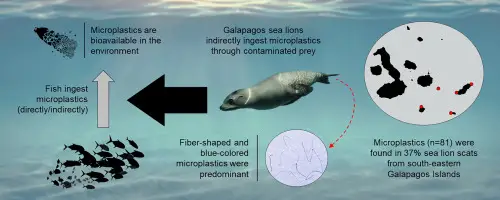
Marine debris pollution poses a significant global threat to biodiversity, with plastics being the primary debris type found in oceans due to their low-cost production and high demand worldwide.
Underwater kleptoparasitims on a human diver by a Galapagos Flightless Cormorant Nannopterum harrisi
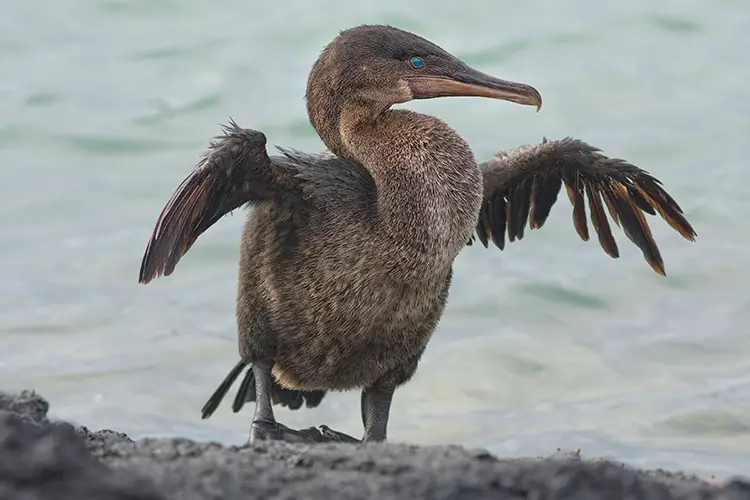

We describe underwater kleptoparasitism on a human diver by a Galapagos Flightless Cormorant Nannopterum harrisi, a behavior that has not been previously described for this species.
Water security and agricultural systems in the Galapagos Islands: vulnerabilities under uncertain future climate and land use pathways
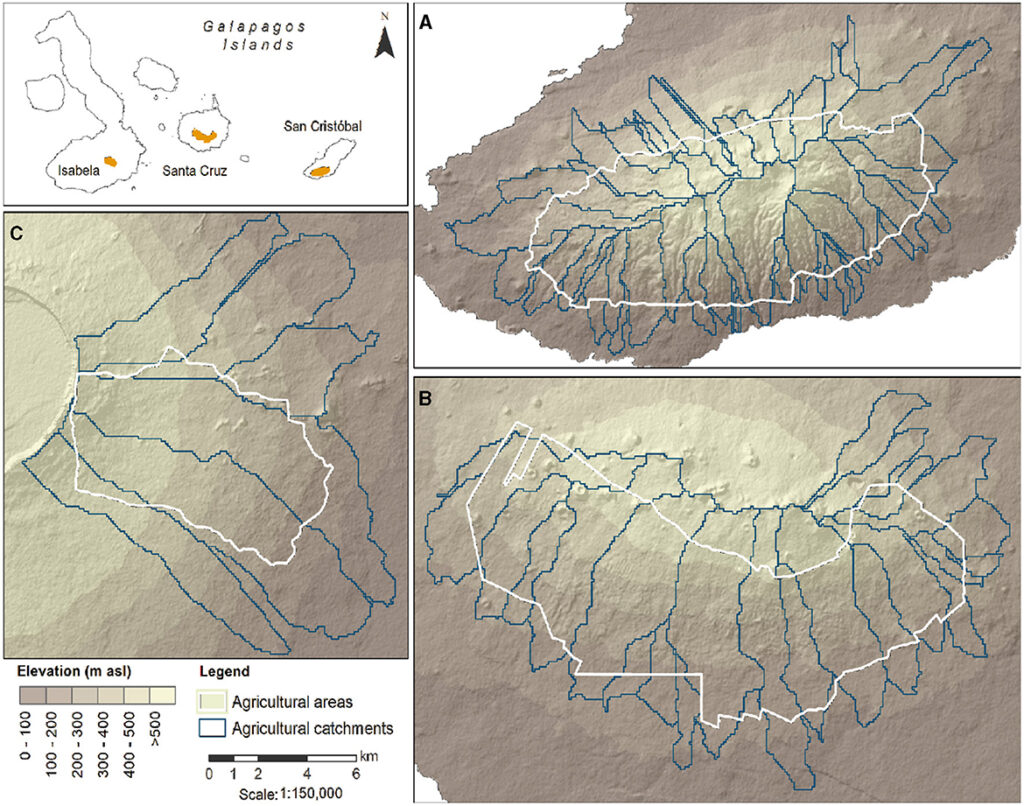
The Galapagos Islands, a hotspot of ecological richness, face challenging climatic and development conditions which undermine regional water security.
Health status of the red-billed tropicbird (Phaethon aethereus) determined by hematology, biochemistry, blood gases, and physical examination
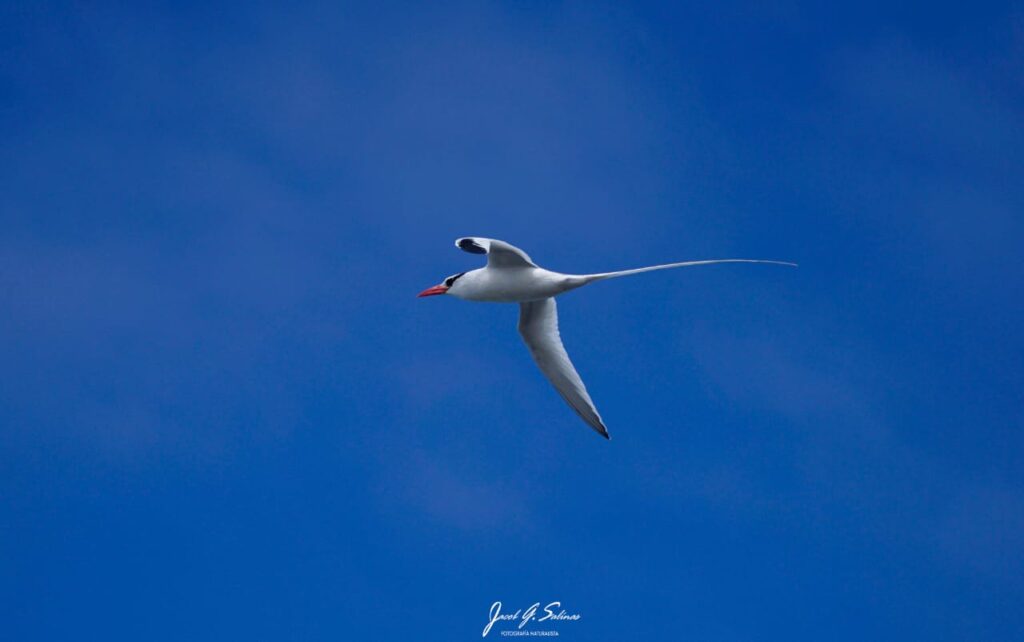

The baseline data, and reference intervals reported in this paper are essential to detecting changes in the health of this seabird in the future.
Movement and vertical habitat use of yellowfin tuna Thunnus albacares in a vertical compressed habitat: the Galápagos Marine Reserve
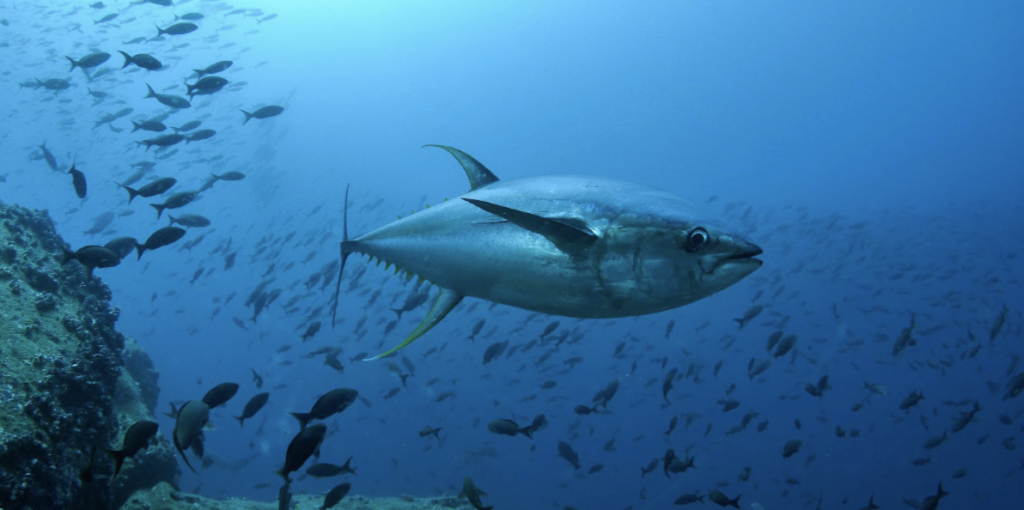

Tropical pelagic predators are exploited by fisheries and their movements are influenced by factors including prey availability, temperature, and dissolved oxygen levels.
When the Archaeologists Leave
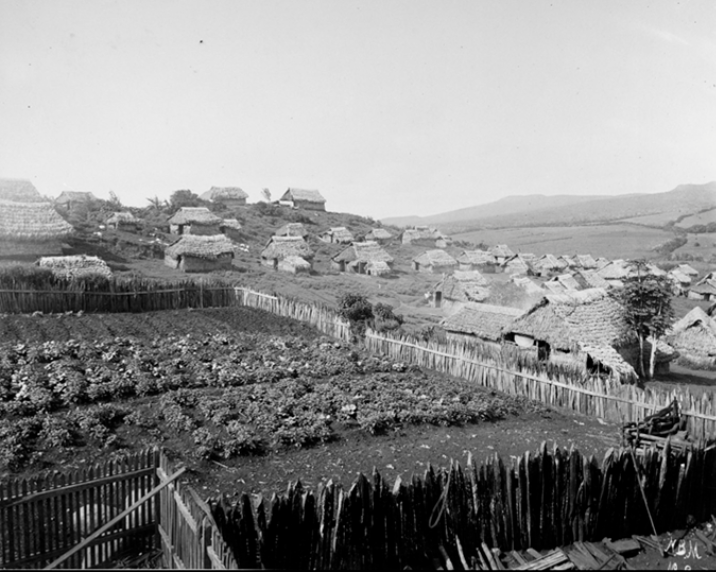

The Hacienda El Progreso functioned as an agro-industrial enterprise in the late nineteenth century. Operating out of San Cristóbal Island in the Galápagos archipelago, the plantation exported refined sugar, coffee, cattle products, and other goods to national and international markets. The plantation established the first permanent human settlement on the island.


